Imagine every person in your organization has “…and continuous improvement specialist” in their job title. That’s what you’re aiming for with lean transformation. It means investing in your people and as a result you’ll build resilience into your process improvement system.
A simple and effective starting point is basic problem-solving skills, and incidents are a natural opportunity to develop these skills. Before an incident occurs, each team member should understand the trigger to investigate. Once that is established, team members should be equipped to respond. That means developing problem-solving skills in every employee at every level, actively encouraging collaboration, and taking action on the insights.
Assemble a team for process improvement
The first step, once the incident is under control, is to assemble a cross-functional team of individuals. For example: a team leader, a team member plus representatives from Quality and Maintenance. Each person brings different perspectives and experience to build a more robust understanding of the situation.
Identify possible causes
An Ishikawa diagram (also known as a fishbone diagram) is useful for determining possible contributing factors for each cause. The causes are typically categorized as Machine, Method and Material, Measurement and Person. Everyone should be encouraged to participate, and don’t hold back. There could be multiple contributing factors and you want to capture all possibilities.
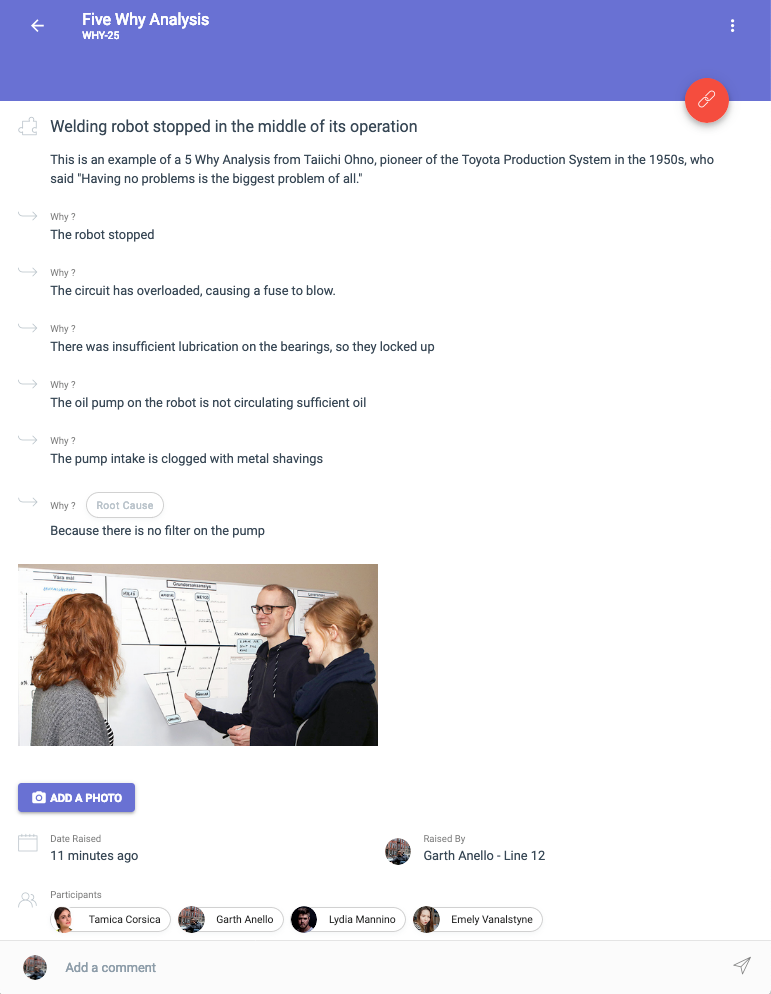
Determine root causes
Circle the most likely contributing factors and perform a 5 Why Analysis for each. This really is as simple as it sounds. Ask “Why?” and after each answer ask “Why?” again, until you’ve exhausted the possibilities. Of course, you’re not limited to asking 5 times – it’s a guide to the depth of analysis you should do.
Prioritise and investigate
After completing all the 5 Whys, and identifying the root causes, you need to follow up with actions. The aim is prevent the incident ever occurring again. With that in mind, it may require education, regular inspection or further investigation. For example:
- Actions – to confirm a hypothesis or perform further investigation
- One Point Lesson – to educate team members about best practice
- Improvement – that could help avoid the situation altogether
- Checklist – for a routine inspection or preventative maintenance
- A3 report – for deeper analysis, investigation and resolution
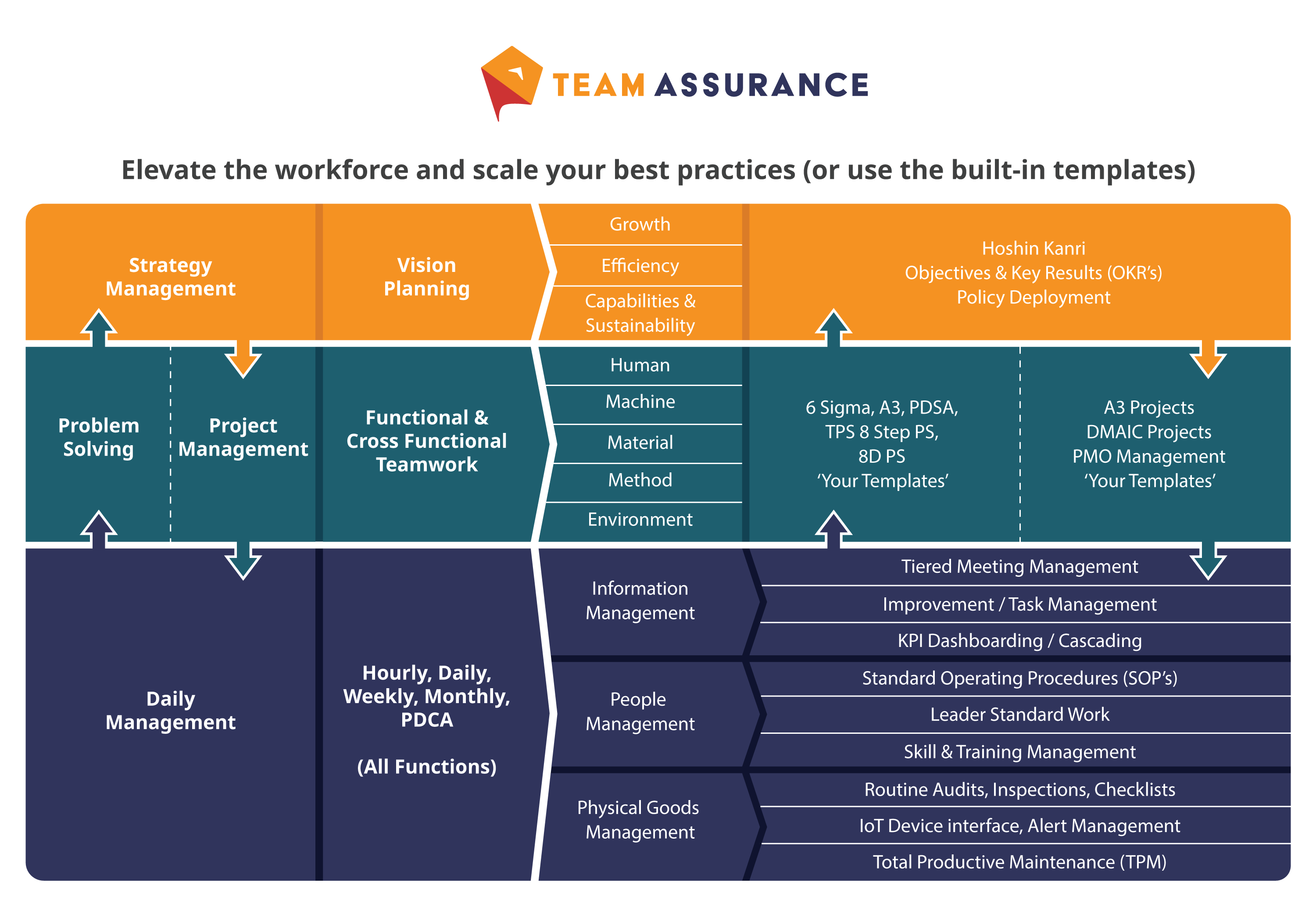
Process Improvement is Part of a greater C.I. framework not just an Isolated Island
Les outils Lean tels que les techniques standardisées de résolution des problèmes, les procédures opérationnelles normalisées (POS) et un processus de gestion quotidienne par paliers qui soutient l'ensemble de la boucle PDCA sont essentiels à la réussite de l'amélioration continue. Toutefois, les organisations doivent veiller à ce que les normes et les processus soient élaborés ensemble, et non de manière isolée. Si l'on ne tient pas compte de tous les processus adjacents, on peut aboutir à un mauvais alignement des personnes, à des silos d'information et à des procédures non optimales.
L'illustration ci-dessous montre comment nous avons conçu la plateforme interconnectée TeamAssurance pour éviter les "solutions ponctuelles" (numériques ou analogiques) optimisées localement et déconnectées qui n'aident pas, et peuvent même entraver la progression vers vos objectifs.
TeamAssurance is an Operational Excellence platform that helps teams with process improvement. If you’re a business in need (or a consultant with clients in need) and you’d like to explore the opportunities that digital-aids to Lean tools provide contact us for a demonstration of the TeamAssurance platform today.